How recent tax changes may affect the FEIE Standard Deduction
Wiki Article
The Foreign Earned Earnings Exclusion Explained: A Guide to Enhancing Your Conventional Deduction
The Foreign Earned Earnings Exclusion (FEIE) is a necessary tax obligation stipulation for united state people and resident aliens living abroad. It permits eligible migrants to omit a significant section of their foreign-earned earnings from federal tax obligations. Recognizing the nuances of FEIE can result in substantial tax financial savings. Nonetheless, lots of individuals neglect essential details that can impact their eligibility and benefits. Exploring these facets may reveal possibilities for improved tax results.Understanding the Foreign Earned Revenue Exclusion
Although several migrants look for opportunities abroad, understanding the Foreign Earned Revenue Exclusion (FEIE) is necessary for managing their tax responsibilities. This stipulation enables united state residents and resident aliens living overseas to exclude a certain quantity of their gained income from federal taxes. The FEIE was developed to reduce the tax obligation burden on individuals that reside outside the United States, recognizing the unique monetary obstacles they might deal with.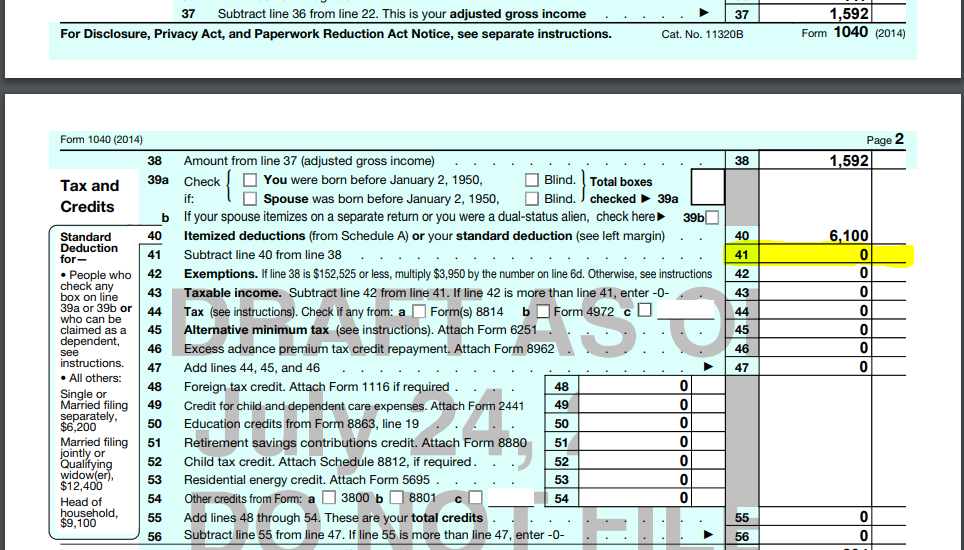
Eligibility Needs for FEIE

Exactly how to Assert the FEIE
To effectively claim the Foreign Earned Revenue Exclusion (FEIE), taxpayers have to first confirm their qualification based on details requirements - FEIE Standard Deduction. The process includes several actions, including submitting the appropriate kinds and offering essential paperwork. Understanding these procedures and requirements is vital for optimizing tax benefits while living abroadQualification Requirements
Qualification for the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) pivots on meeting certain criteria set by the internal revenue service. To qualify, people must be U.S. people or resident aliens who gain income while functioning abroad. They require to establish a foreign tax obligation home, which means their main place of service is outside the USA. Additionally, candidates should satisfy either the Authentic Residence Examination or the Physical Presence Test. The Bona Fide Home Examination requires that a taxpayer resides in a foreign nation for a whole tax obligation year, while the Physical Presence Test requires costs at the very least 330 complete days in a foreign country during a 12-month duration. Fulfilling these requirements is crucial for claiming the FEIE.Filing Process Steps
Just how can one efficiently browse the process of asserting the Foreign Earned Income Exemption (FEIE)? Individuals need to establish their eligibility based on the physical presence test or the bona fide residence test. When verified, they must finish IRS Type 2555, which information international revenue and residency. This form should be affixed to their yearly income tax return, usually Kind 1040. It is important to accurately report all foreign made earnings and warranty conformity with the internal revenue service standards. In addition, taxpayers should maintain proper documentation, such as foreign tax returns and evidence of residency. By adhering to these steps, individuals can successfully declare the FEIE and possibly minimize their gross income significantly, boosting their overall financial setting.Determining Your Foreign Earned Earnings Exemption
While many expatriates seek to optimize their economic advantages abroad, recognizing the estimation of the Foreign read this Earned Revenue Exemption is necessary for precise tax obligation coverage. The Foreign Earned Earnings Exemption allows qualifying people to leave out a particular amount of their foreign profits from U.S. taxation, which is adjusted annually for inflation. To compute this exemption, expatriates need to identify their overall foreign earned revenue, which usually consists of earnings, wages, and professional charges earned while living in an international country.Next off, they must complete internal revenue service Type 2555, supplying details regarding their international residency and work standing. FEIE Standard Deduction. It is very important to fulfill either the bona fide home examination or the physical presence test to certify for the exemption. Once these aspects are developed, the maximum permitted exemption quantity is applied, minimizing the person's taxable earnings substantially. Accurate computations can bring about substantial tax cost savings for migrants living and working abroad
The Impact of FEIE on Other Tax Obligation Advantages
The Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) can affect an individual's eligibility for sure tax obligation benefits, consisting of the common deduction. By omitting international earned earnings, taxpayers might locate their adjusted gross revenue affected, which consequently can affect their qualification for numerous tax obligation credit scores. Recognizing these interactions is vital for enhancing tax obligation outcomes while living abroad.Communication With Criterion Deduction
When people receive the Foreign Earned Revenue Exclusion (FEIE), their qualification for the conventional deduction may be impacted, potentially altering their total tax obligation responsibility. The FEIE permits taxpayers to leave out a particular quantity of made earnings from U.S - FEIE Standard Deduction. taxation, which can lead to a lowered gross income. As an outcome, if the left out earnings surpasses the basic deduction, it can lessen the advantage of declaring that deduction. In addition, taxpayers that make use of the FEIE might discover that their capacity to detail reductions is additionally affected, as particular expenditures might be affected by the exemption. Understanding this communication is essential for expatriates to maximize their tax benefits while guaranteeing conformity with united state tax obligation regulationsQualification for Tax Obligation Credit Scores
Steering via the intricacies of tax obligation credit reports can be challenging for migrants, particularly since the Foreign Earned Revenue Exclusion (FEIE) can substantially affect eligibility for these benefits. The FEIE permits qualified people to exclude a substantial section of their international profits from united state taxation, yet this exclusion can likewise affect access to numerous tax credit ratings. For example, taxpayers who use the FEIE might find themselves ineligible for credits like the Earned Earnings Tax Obligation Credit Report (EITC), as these credit scores commonly require gross income. Additionally, the exclusion might limit the capability to assert certain deductions or credit scores related to dependents. Understanding the interaction in between the FEIE and available tax obligation credit scores is necessary for migrants aiming to optimize their tax situation.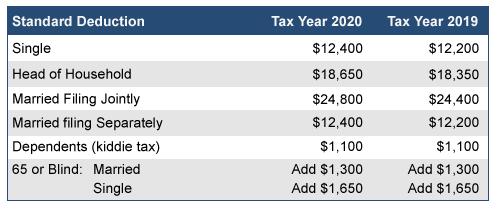
Typical Errors to Prevent When Claiming FEIE
Commonly, expatriates experience a number of mistakes while asserting the Foreign Earned Earnings Exclusion (FEIE), which can cause expensive errors or use this link missed out on chances. One constant error is stopping working to meet the physical presence or authentic house test, which is crucial for eligibility. Additionally, expatriates usually neglect the need to file Type 2555 appropriately, resulting in incomplete a knockout post or imprecise entries.Another usual mistake includes improperly calculating international gained income, as several do not represent all appropriate earnings resources. Some migrants mistakenly assume they can omit all their earnings, uninformed of the constraints on the exemption quantity. Furthermore, overlooking to preserve appropriate paperwork, such as travel dates and residency standing, can threaten a case. Misinterpreting the ramifications of the FEIE on other tax credit histories may lead to unintentional tax liabilities. Recognition of these challenges can promote a smoother asserting procedure and make best use of potential advantages.
Resources for Expats Navigating United State Taxes
Maneuvering U.S. tax obligation commitments can be testing for expatriates, especially after encountering mistakes in claiming the Foreign Earned Revenue Exemption (FEIE) To assist navigate these complexities, a selection of sources are readily available. The internal revenue service site offers considerable details on tax obligation guidelines, faqs, and forms especially customized for expatriates. Additionally, companies like the American Citizens Abroad (ACA) and the Deportee Tax obligation Professionals offer advice and support to ensure compliance with tax obligation legislations.On the internet forums and areas, such as the Deportee Online forum, permit expatriates to share experiences and understandings, promoting an encouraging atmosphere for those encountering similar obstacles. Tax obligation preparation software application, like copyright and H&R Block, often includes attributes made for expats, making the declaring procedure more easy to use. Involving with these resources can equip migrants to much better understand their tax commitments and optimize advantages like the FEIE.
Often Asked Questions
Can I Declare FEIE if I'M Independent Abroad?
Yes, self-employed individuals abroad can claim the Foreign Earned Revenue Exemption (FEIE) To qualify, they need to meet particular demands regarding residency and revenue, guaranteeing they adhere to internal revenue service guidelines for expatriates.
Is the FEIE Applicable to Foreign Pensions?
The Foreign Earned Revenue Exemption (FEIE) is not suitable to international pensions. Pensions are considered unearned income and do not get approved for the exemption, which especially puts on made income from employment or self-employment abroad.What Takes place if I Go Back To the U.S. Mid-Year?
If a private returns to the united state mid-year, they might need to adjust their tax obligation scenario. Their qualification for specific deductions and exemptions, consisting of the Foreign Earned Earnings Exemption, can be influenced by their residency condition.Can FEIE Be Claimed With Various Other Deductions?
Yes, the Foreign Earned Income Exemption (FEIE) can be declared alongside various other reductions. Treatment should be taken to guarantee appropriate compliance with tax obligation guidelines, as certain constraints may use based on private conditions.Exactly How Does FEIE Affect State Tax Obligation Commitments?
The Foreign Earned Income Exemption can minimize a taxpayer's federal earnings tax liability, but it does not automatically affect state tax commitments, which differ by state and may still require coverage of foreign earnings.Several migrants look for chances abroad, comprehending the Foreign Earned Earnings Exclusion (FEIE) is essential for managing their tax commitments. By omitting foreign earned earnings, taxpayers may discover their adjusted gross revenue affected, which in turn can impact their credentials for numerous tax obligation credit scores. Steering through the intricacies of tax credit scores can be challenging for expatriates, particularly considering that the Foreign Earned Revenue Exemption (FEIE) can significantly impact qualification for these benefits. Taxpayers that utilize the FEIE might discover themselves disqualified for credits like the Earned Earnings Tax Obligation Credit (EITC), as these credit ratings typically call for taxed revenue. Steering U.S. tax obligation obligations can be testing for expatriates, particularly after running into mistakes in claiming the Foreign Earned Earnings Exclusion (FEIE)
Report this wiki page